In this way, the current accounting period (or any other accounting period) can be made to appear better. Liquidity ratios are needed to check if the company is liquid enough to settle its debts and pay back any liabilities. Horizontal analysis makes it easy to detect these changes and compare growth rates and profitability with other companies in the industry.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Prior to publication, articles are checked thoroughly for quality and accuracy. Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs. CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path.
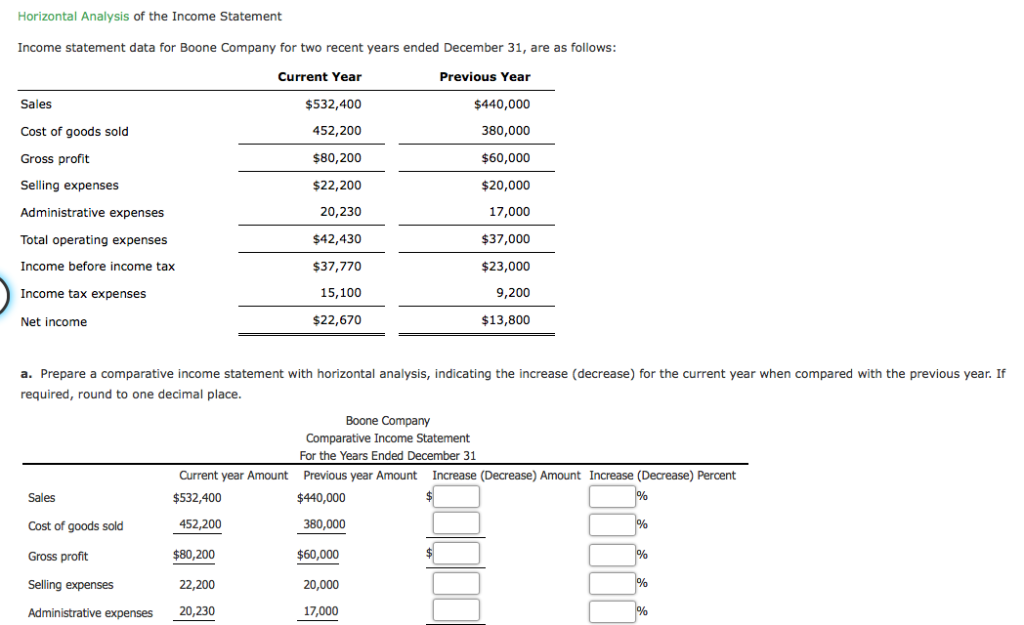
Horizontal Analysis of Financial Statements
- Horizontal and vertical analysis are commonly used by financial analysts, investors, and managers to gain insight into a company’s financial performance and to make informed decisions based on the analysis.
- Insert a column to the right of ‘2022’ and click on the cell corresponding to the first line item.
- This metric is especially useful for identifying seasonal trends or the impact of market conditions on the company’s performance.
- Different ratios, such as earnings per share (EPS) or current ratio, are also compared for different accounting periods.
- Changes between the income from operations and net income lines can be reviewed to identify the reasons for the relatively lower increase in net income.
You’ve got your numbers, you’ve done the math, but there are still some landmines that can blow up your carefully crafted analysis. First, we noted that Colgate had not provided segmental information in the income statement. However, as additional information, Colgate has provided some details of segments on page 87.
Example 2: Analyzing Revenue Growth
Horizontal analysis is used to improve and enhance these constraints during financial reporting. Horizontal analysis, or “time series analysis”, is oriented around identifying trends and patterns in the revenue growth profile, profit margins, and/or cyclicality (or seasonality) over a predetermined period. Horizontal analysis is a financial analysis technique used to evaluate a company’s performance over time. By comparing prior-period financial results with more current financial results, a company is better able to spot the direction of change in account balances and the magnitude in which that change has occurred. The primary difference between vertical analysis and horizontal analysis is that vertical analysis is focused on the relationships between the numbers in a single reporting period, or one moment in time. Horizontal analysis looks at certain line items, ratios, or factors over several periods to determine the extent of changes and their trends.
Also, horizontal analysis alone may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health and requires additional analysis and context. Through horizontal analysis of financial statements, you would be able to see two actual data for consecutive years and would be able to compare every item. To perform a horizontal analysis, you must first gather financial information of a single entity across periods of time. Most horizontal analysis entail pulling quarterly or annual financial statements, though specific account balances can be pulled if you’re looking for a specific type of analysis. Vertical analysis, also called common-size analysis, focuses on the relative size of different line items so that you can easily compare the income statements and balance sheets of different-sized companies. Accountants, investors, and business owners regularly review income statements to understand how well a business is doing in relation to its expected future performance and use that understanding to adjust their actions.
Data Tables
For example, to find the growth rate of net sales for 2015, the formula is (Net Sales 2015 – Net Sales 2014) / Net Sales 2014. You do not need special financial skills to ascertain the difference between the previous and last year’s data. However, it would be best if you had diligence, attention to detail, and a logical mind to decipher why the change happens. In conclusion, we’re able to compare the year-over-year (YoY) performance of our company from 2020 to 2021. The latter two tend to go hand-in-hand because the most useful benchmark against which to compare recent performance is most often the preceding period.
An analysis of the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement over time gives a complete picture of operational results and reveals what is driving a company’s performance and whether it is operating efficiently and profitably. Analyzing income statements is a fundamental aspect of financial statement analysis, providing insights into a company’s profitability, revenue generation, and expense management. The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, details revenues, costs of goods sold, operating expenses, and net income over a specific period. By examining trends in these areas, analysts can assess a company’s financial health, efficiency, and growth potential. Understanding how each component impacts overall profitability is essential for investors, creditors, and stakeholders when making informed financial and investment decisions. To understand what has been affecting a company’s financial performance over a period of years, investors and analysts can use horizontal analysis to detect trends and growth patterns.
So grab your calculator and get ready to decode your financial statements like a pro. Vertical analysis expresses each line item on a company’s financial statements as a percentage of a base figure, whereas horizontal analysis is more about measuring the percentage change over a specified period. The analysis can be carried out on any of the financial statements but is usually performed on the balance sheet and income statement together with appropriate accounting ratios. While the horizontal analysis can be performed on each statement in isolation, it is always better to analyse both balance sheet and income statements together to avoid drawing the wrong conclusions about the performance of a business. These changes are either in the form of dollar amount (variance) and percentage. You can calculate these changes by comparing items in the base accounting period with other items in subsequent periods and financial statements.
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, topic no 458 educator expense deduction 2020 budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. By dividing the net difference by the base figure, the percentage change comes out to 25%.